Bookkeeping
What Is a T Account in Accounting and How Is It Used?
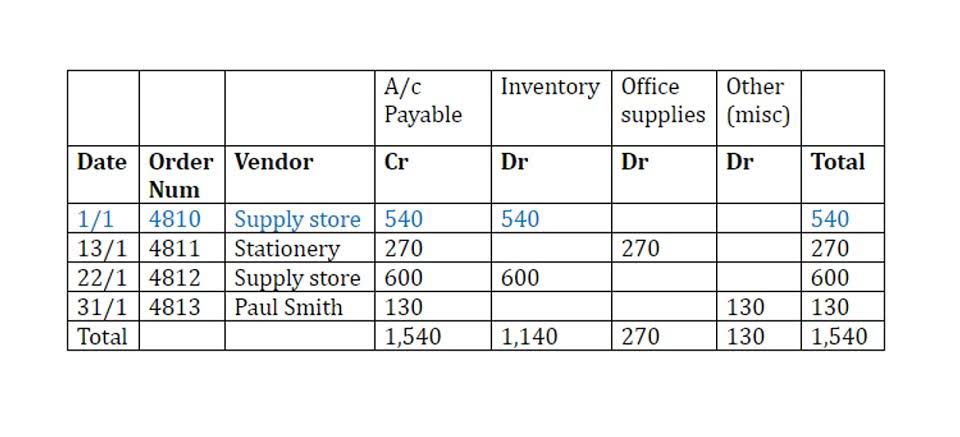
These tools offer a clear and concise way to track their finances without getting bogged down in complex spreadsheets. Debits and credits can be tricky initially, but they’re the foundation of understanding how businesses track their finances. Remember that with every transaction and journal entry there will be two unearned revenue accounts that are affected.

Example of a Transaction
- And for a review of the most common journal entries, see the lesson on basic accounting journal entries.
- T-accounts are like a cheat sheet for seeing how debits and credits balance out.
- Without such analytical tools, businesses may struggle to effectively assess profitability, liquidity, and solvency.
- The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
A double entry system is time-consuming for a company to implement and maintain, and may require additional manpower for data entry (meaning, more money spent on staff). Now you’re equipped to tackle those transactions with confidence, understand your business finances like a pro, and make smarter decisions for the future. As seasoned accountants adapt to new technologies, T accounts can serve as a bridge between their experience and the digital world. For new accounting students raised on software, T accounts provide a familiar and Certified Bookkeeper intuitive way to grasp the underlying logic of accounting. They offer a common language for accountants of all backgrounds to communicate and collaborate effectively.
T-Account vs Trial Balance
- A T-account is used in bookkeeping, which involves keeping track of the financial transactions that occur within a business.
- T-accounts can become unwieldy and inefficient in large-scale operations, such as those of multinational corporations or conglomerates.
- This deeper grasp empowers accountants to analyze financial data with greater confidence and interpret its implications for the business.
- Retained earnings reflect net income and dividends, directly influencing equity.
- You’re a budding entrepreneur who just launched your dog walking service.
- Decreases in assets are recorded by credits, so Cash will be credited for $150.
My inventory is reduced each time I sell a coffee so I need to credit the inventory account by 50p, reducing its value. Due to its simplistic nature, T-accounts are also used as a learning tool to practice transactions and t accounts double-entry accounting. They can be found drawn on a scrap piece of paper to templates made in accounting software.

Working Out An Example of T Accounts

The contra account here used to describe what occurred is baking equipment. As you can see, it’s basically a mirror image of what we recorded in the Bank T account. The above transaction would not only affect the Bank T account but also affect the contra account or second account, Capital.
- Debits represent increases in assets and expenses, and decreases in liabilities and equity.
- With automation handling the heavy lifting, accountants can shift their focus to the bigger picture.
- T-accounts show you what to put in the ledger to keep everything balanced.
- The spreadsheet lets you see how your spending habits impact your overall balance.
- Below is the T-account for Cash for the transactions and events of Xao Corporation.
- On account is saying that the supplies will be paid for later and that is why we increase accounts payable with a liability.
It is called the T-account because bookkeeping entries are shown in a way that resembles the shape of the alphabet T. It depicts credits graphically on the right side and debits on the left side. Each example of the T-account states the topic, the relevant reasons, and additional comments as needed. T-accounts can also be used to record changes to the income statement, where accounts can be set up for revenues (profits) and expenses (losses) of a firm. For the revenue accounts, debit entries decrease the account, while a credit record increases the account.


